Custom Functions
About Custom Functions
Administrators can use custom functions in Index Fields Maintenance to modify data used with documents when they are processed.
For example, date field formats may vary from document to document. By entering functions for each document, you can ensure the final date format used in your imaging system indexing is the same for all documents.
Refer to Index Fields Maintenance for information on entering and editing functions.
Order of Precedence
When documents are processed, functions are applied in the following order:
- Custom Function 1
- Custom Function 2
- Custom Function 3
- Custom Function 4
Constants
- COMMA = “,”
- EQUALS = “=”
- NOSPACE = “”
Monikers
- %ShortName% - Short name of document
- %DocumentName% - Long name of document
- %CurrentIndex%
Functions
Note:
Spaces are not allowed in functions.
Standard VB date and time formats apply.
GETCURRENTDATETIME
This function returns the current date/time in the specified format.
- GETCURRENTDATETIME(FORMAT)
- FORMAT: HH:mm:ss = 14:00:01; MM/dd/yy = 01/01/10
- Example
- GETCURRENTDATETIME(HH:mm:ss): Will return the current time in 24 hour format
- GETCURRENTDATETIME(MM/dd/yy): Will return the current date as “01/01/10”
LOOKUP
This function is used to look up any index field value in a parameter file to replace the input string in index builder string.
Refer to %Lookup() for function usage.
For use as an Indexing function (Index Fields Maintenance), the Lookup function must start with "@". Monikers will use % in this case.
Indexing Examples
-
@Lookup(%CurrentIndex%,Parameters.txt,COMMA,1,False)
-
@Lookup(%DocumentName%,Parameters.txt,COMMA,1,False)
-
@Lookup(%ShortName%,Parameters.txt,COMMA,1,True)
MODIFYDATETIMEFORMAT
This function returns the index value in the given date/time format.
- MODIFYDATETIMEFORMAT(Format)
- MODIFYDATETIMEFORMAT(HH:mm:ss:fffffff): Will return the current time in 24 hour format
- Example:
- MODIFYDATETIMEFORMAT(HH:mm:ss): Will return the current time in 24 hour format
- MODIFYDATETIMEFORMAT(MM/dd/yy): Will return the current date as “01/01/10”
REMOVELEADINGCHARS
This function checks the first character on the left side of the input index. The first character is deleted if it matches character_to_seek. This process is repeated until the character is not found or the string is empty.
Some characters cannot be expressed using the ASCII representation. Instead, they must be denoted as a special keyword as follows:
| Special Characters | ASCII Representation | Keyword |
|---|---|---|
| Comma | , | COMMA |
| Equal Sign | = | EQUAL or EQUALS |
| Plus Sign | + | PLUS |
| Space | SPACE |
-
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(character_to_seek)
-
Examples:
Function
Description
Index Input
Index Result
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(0)
The function removes “0” at the beginning of the input index.
00003234
3234
000030000
3000
000000000
Nothing
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(X)
The function removes “X” at the beginning of the input index. If there are none, the input index remains the same.
X00003234
00003234
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(1)
The function removes “1” at the beginning of the input index. If there are none, the input index remains the same.
100003111
00003111
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(PLUS)
The input function removes “+” at the beginning of the function.
+1234
1234
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(SPACE)
The function removes all spaces at the beginning of the input index.
3234
3234
REMOVELEADINGCHARS(COMMA)
The function removes all commas at the beginning of the input index.
,Nelson Jordan
Nelson Jordan
REPLACECHARS
This function is used to replace single or multiple characters in the index value.
- REPLACECHARS(CharsToReplace=ReplacedChar) - single character replacement
- REPLACECHARS(x1=y1,x2=y2,x3=y3,...,xn=yn) - multiple character replacements
- Characters are case sensitive
- CharsToReplace
Any character, set of characters or the keyword “COMMA”
If the constant (REMOVEALPHACHARS) is used, the function will replace alphabetic characters ([a-z] or [A Z]) with ReplacedChar.
If the constant (REMOVENUMERICCHARS) is used, the function will replace numeric characters([0-9]) with ReplacedChar.
To replace a backslash “\”, the CharsToReplace must be “\\”.
- Replaced Char:
Any set of characters, keyword “COMMA”, keyword “NOSPACE” or keyword “EQUALS”.
If no value is used, then a space will be used as the ReplacedChar.
- Examples:
REPLACECHARS(REMOVEALPHACHARS=1): Will replace all alpha characters with the numeral “1”.
REPLACECHARS(REMOVENUMERICCHARS=A): Will replace all numeric characters with the character “A”.
REPLACECHARS(Test=): Will replace the word “Test” with a space.
REPLACECHARS(\\=A): Will replace a backslash (\) with the character “A”.
REPLACECHARS(Server\\=): Will replace “Server\” with a space.
REPLACECHARS(A=B,U=Z): Will replace all occurrences of "A" with "B" and "U" with "Z".
REPLACECHARS(A=B,U=COMMA): Will replace all occurrences of "A" with "B" and "U" with a comma ",".
RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH
This function is used to return a fixed width for the specified index field padded with the specified characters.
- RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(FixedLength,Align,AppendChars,Truncate)
- FixedLength: Required. The number of characters fixed width for this index field. [Required]
- Align: Optional. Right or Left (not case-sensitive) [Default: Left]
- AppendChars: Optional. Character appended to the field to achieve the FixedLength value. Any Alpha-Numeric character is allowed. [Default: 0]
- When the entire parameter is omitted, the default character is 0.
- Presence of the separating comma with no character will be interpreted as a space.
- The constant “COMMA” can be used insert a comma “,”.
- Truncate: Optional. If the FixedLength of the index field is less than the existing field length, the field can be truncated with the following options [Default: Not Used]:
- TruncateLeft: Remove characters from the left side of the index field value.
- TruncateRight: Remove characters from the right side of the index field value.
- If parameters 2, 3 and 4 are not provided, the default alignment will be “Left”, any appended character will be “0” and no truncate will apply.
- Examples:
- RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(30): The index field length will be 30 characters with zeros (0) added to the left of the original value. (No value for Align: Left is used. No value for AppendChars: 0 is used. No value for Truncate: Not used.)
{“123” Þ “000000000000000000000000000123”} - RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(30,Right): The index field length will be 30 characters with zeros (0) added to the right of the original value. (No value for AppendChars: 0 is used. No value for Truncate: Not used.)
{“123” Þ “123000000000000000000000000000”} - RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(30,Left,): The index field length will be 30 characters with spaces added to the left of the original value. (No value for Truncate: Not used.)
{“123” Þ “ 123”} - RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(15,Left,0,TruncateLeft)
{“987659876598765123” Þ “659876598765123”}
- RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(30): The index field length will be 30 characters with zeros (0) added to the left of the original value. (No value for Align: Left is used. No value for AppendChars: 0 is used. No value for Truncate: Not used.)
SPLIT
The SPLIT function returns a substring before or after a selected character or string.
- SPLIT([BEFORE or AFTER],SplitCharacter,ReturnElement)
- BEFORE or AFTER: The direction of the substring from the SplitCharacter.
- SplitCharacter: The character or string in the IndexValue used to separate sub strings.
1. The space character “ “ is a valid character. (BEFORE, ,2)
2. The comma character “,“ is not a valid character. (BEFORE,,,2). For these instances, use REPLACECHAR to substitute a different character.
- ReturnElement: The element returned before or after the split character.
- Examples
Sample Field Value: First-Second-Third-Fourth- SPLIT(BEFORE,-,0) Not Supported
(Zero is not used as an element counter.) - SPLIT(AFTER,-,0) Not Supported
(Zero is not used as an element counter.) - SPLIT(BEFORE,-,1) Returns “First”
(The element before the first separator.) - SPLIT(AFTER,-,1) Returns “Second”
(The element after the first separator.) - SPLIT(BEFORE,-,2) Returns “Second”
(The element before the second separator.) - SPLIT(AFTER,-,2) Returns “Third”
(The element after the first separator.) - SPLIT(BEFORE,-,3) Returns “Third”
(The element before the third separator.) - SPLIT(AFTER,-,3) Returns “Fourth”
(The element after the third separator.) - SPLIT(BEFORE,-,4) Not Supported
(There is no fourth separator.) - SPLIT(AFTER,-,4) Not Supported
(There is no fourth separator.)
- SPLIT(BEFORE,-,0) Not Supported
SPLITALL
The SPLITALL function returns everything before or after a selected character or string.
- SPLITALL([BEFORE or AFTER],SplitCharacter,ReturnElement)
- BEFORE or AFTER: The direction of the substring from the SplitCharacter.
- SplitCharacter: The character or string in the IndexValue used to separate sub strings.
1. The space character “ “ is a valid character. (BEFORE, ,2)
2. The comma character “,“ is not a valid character. (BEFORE,,,2). For these instances, use REPLACECHAR to substitute a different character. - ReturnElement: The delimiter count used in splitting.
- Examples:
Sample Field Value: First-Second-Third-Fourth- SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,0) Not Supported
(There is no split character in the 0 position; cannot go before.) - SPLITALL(AFTER,-,0) Returns “First-Second-Third-Fourth”
(There is no split character in the 0 position. The entire string after the beginning delimiter is returned.) - SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,1) Returns “First”
(The full substring before the first separator.) - SPLITALL(AFTER,-,1) Returns “Second-Third-Fourth”
(The full substring after the first separator.) - SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,2) Returns “First-Second“
(The full substring before the second separator.) - SPLITALL(AFTER,-,2) Returns “Third-Fourth“
(The full substring after the second separator.) - SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,3) Returns “First-Second-Third“
(The full substring before the third separator.) - SPLITALL(AFTER,-,3) Returns “Fourth (The full substring after the third separator.)
- SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,4) Returns “First-Second-Third-Fourth“
(There is no “-“ character in the fourth position. The entire string before the end delimiter is returned.) - SPLITALL(AFTER,-,4) Not supported
(There is no split character in the fourth position. ) - SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,5[6,7,etc.]) Returns “First-Second-Third-Fourth“
(There is no “-“ character in the these positions. The entire string before the end delimiter is returned.)
- SPLITALL(BEFORE,-,0) Not Supported
Additional Examples
Example 1
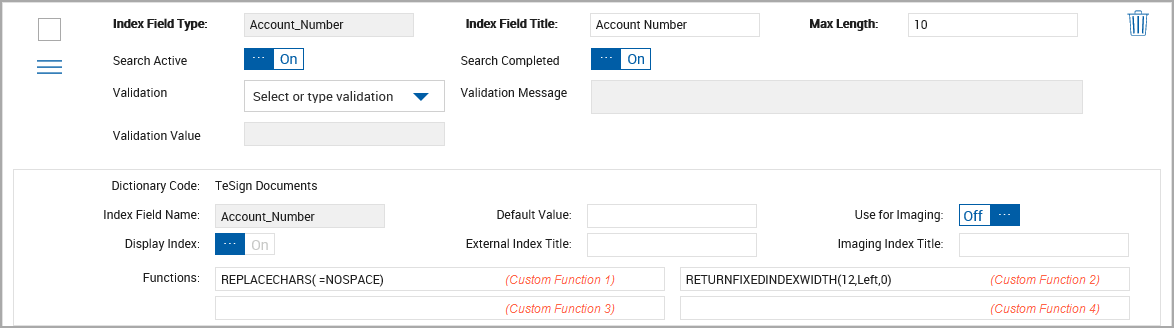
In this example, we added 2 custom functions to the Account Number index field for the TeSign Documents dictionary. If your installation used multiple dictionaries, the custom functions may need to be applied for all dictionaries.
Functions are applied in order: Custom Function 1, Custom Function 2, Custom Function 3, Custom Function 4.
Using “123-45-6789” as the original data supplied to eSign.
Custom Function 1 “REPLACECHARS(-=NOSPACE)” results in the value “123456789”.
Custom Function 2 is then applied to the results of Custom Function 1 and “RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(12,Left,0)” results in a final value “000123456789”.
Example 2
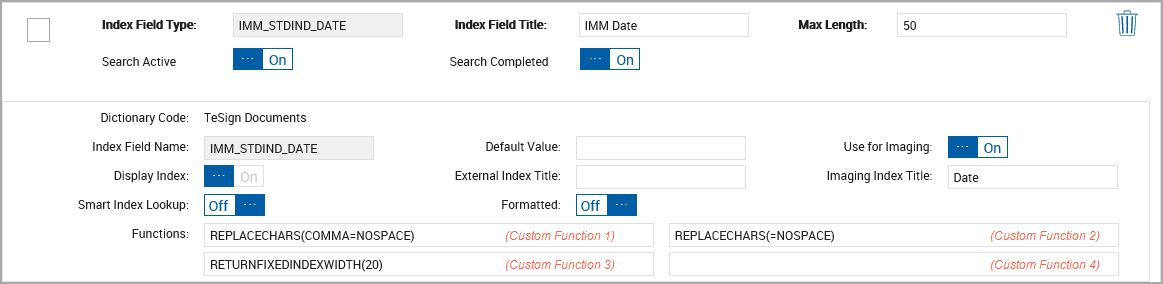
In this example, we added 3 custom functions.
Functions are applied in order: Custom Function 1, Custom Function 2, Custom Function 3, Custom Function 4.
Using a long birth date of “September 22, 1987” as the original data supplied to eSign.
Custom Function “REPLACECHARS(COMMA=NOSPACE)” results in “September 22 1987”.
Custom Function “REPLACECHARS(=NOSPACE)” results in “September221987”.
Custom Function “RETURNFIXEDINDEXWIDTH(20)” results in “00000September221987”.